What reasons in this passage support using genetically modified foods sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the compelling arguments in favor of genetically modified foods, examining their potential benefits, environmental impact, economic considerations, and ethical implications.
As we delve into the intricacies of genetic modification, we uncover a wealth of evidence supporting the use of these foods. From enhanced crop yields to increased nutritional value, the advantages of genetically modified foods are undeniable. Moreover, their resistance to pests and diseases offers significant environmental benefits, reducing the need for harmful pesticides and herbicides.
Benefits of Genetically Modified Foods
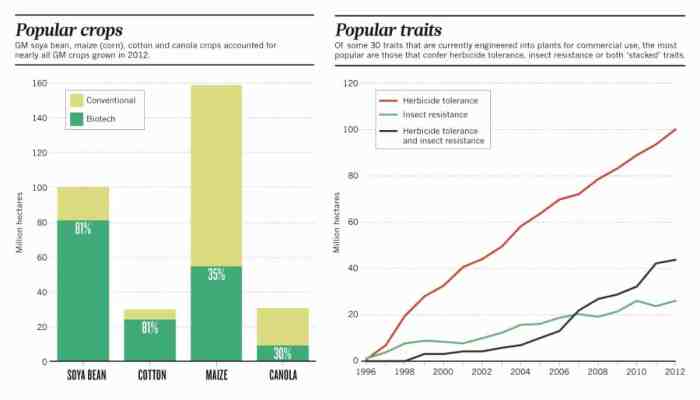
Genetically modified (GM) foods have been developed to improve crop yields, nutritional value, and resistance to pests and diseases. These advancements have significant implications for global food security and sustainability.
Increased Crop Yields
GM crops have been engineered to produce higher yields, enabling farmers to grow more food on the same amount of land. For example, GM soybeans have increased yields by 20-30%, providing a substantial boost to global soybean production.
Nutritional Enhancements
GM foods can be fortified with essential nutrients, addressing malnutrition in developing countries. Golden rice, for instance, is genetically modified to produce beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, helping combat vitamin A deficiency.
Enhanced Pest and Disease Resistance
GM crops have been developed with built-in resistance to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides. This not only lowers production costs for farmers but also minimizes environmental pollution and promotes soil health.
Environmental Impact of Genetically Modified Foods

The environmental impact of GM foods is a subject of ongoing research and debate. While some concerns have been raised, there is evidence to suggest that GM crops can have positive environmental effects.
Reduced Pesticide and Herbicide Use, What reasons in this passage support using genetically modified foods
GM crops resistant to pests and diseases require fewer chemical inputs, reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. This has led to significant reductions in pesticide and herbicide use, minimizing pollution and promoting biodiversity.
Soil Conservation
GM crops with improved drought tolerance and resistance to soil erosion can contribute to soil conservation. By reducing the need for irrigation and tilling, these crops help preserve soil structure and prevent soil degradation.
Potential Impact on Biodiversity
While concerns have been raised about the potential impact of GM crops on biodiversity, research suggests that the effects are generally minimal. In fact, GM crops resistant to pests and diseases can reduce the need for broad-spectrum pesticides, which can have negative effects on beneficial insects and other wildlife.
Economic Considerations of Genetically Modified Foods
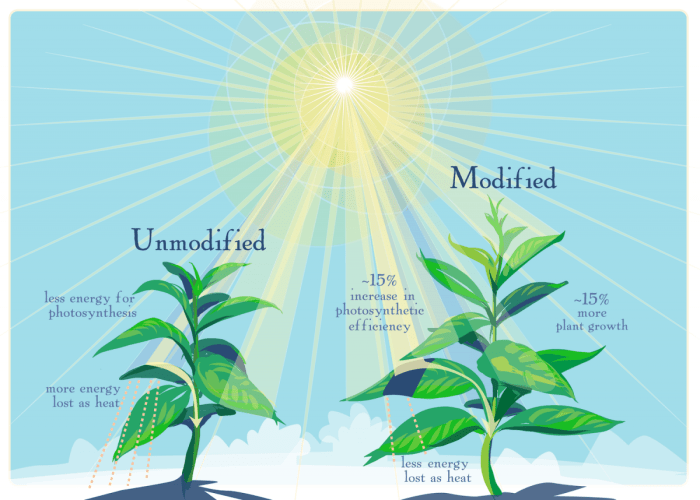
GM foods have significant economic implications for farmers, consumers, and the global food supply.
Cost-Effectiveness for Farmers
GM crops with improved yields and resistance to pests and diseases can reduce production costs for farmers. This can increase their profitability and improve their livelihoods.
Potential Economic Benefits for Consumers
GM foods with enhanced nutritional value can improve public health and reduce healthcare costs. Fortified crops, such as Golden rice, can address malnutrition and reduce the incidence of nutrient deficiencies.
Impact on Global Food Security
GM crops have the potential to increase global food production and improve food security. By increasing crop yields and reducing losses due to pests and diseases, GM foods can help meet the growing demand for food in a sustainable way.
Ethical and Societal Concerns
The use of GM foods raises ethical and societal concerns that require careful consideration.
Ethical Concerns
Some individuals have ethical concerns about the genetic modification of food, questioning its long-term effects on human health and the environment. Others express concerns about the potential impact on biodiversity and the rights of future generations.
Societal Debates
The use of GM foods has sparked societal debates, with some groups advocating for their widespread adoption and others calling for caution and further research. These debates involve issues such as transparency, consumer choice, and the role of science in food production.
Importance of Transparency and Consumer Choice
Transparency and consumer choice are crucial in addressing ethical and societal concerns. Consumers should have access to accurate information about GM foods and the ability to make informed decisions about whether or not to consume them. Clear labeling and responsible marketing practices are essential for ensuring consumer confidence and trust.
Key Questions Answered: What Reasons In This Passage Support Using Genetically Modified Foods
What are the primary benefits of genetically modified foods?
Genetically modified foods offer several key benefits, including increased crop yields, enhanced nutritional content, and increased resistance to pests and diseases.
How do genetically modified foods contribute to environmental sustainability?
Genetically modified crops can reduce the need for pesticides and herbicides, thereby minimizing environmental pollution and promoting soil conservation.
Are there any ethical concerns associated with genetically modified foods?
Ethical concerns surrounding genetically modified foods include potential risks to human health and the environment, as well as issues related to intellectual property rights and consumer choice.