Criticism of structuralism in psychology – Structuralism, a prominent school of thought in psychology, has faced significant criticism for its limitations, reductionist approach, and lack of ecological validity. This article delves into the critiques of structuralism, exploring its shortcomings and implications for the field of psychology.
Structuralism’s focus on observable behavior, breaking down mental processes into smaller components, and reliance on introspection as a research method have been criticized for their limitations. Critics argue that this approach oversimplifies complex psychological phenomena and fails to capture the dynamic and holistic nature of the mind.
Criticism of Structuralism in Psychology
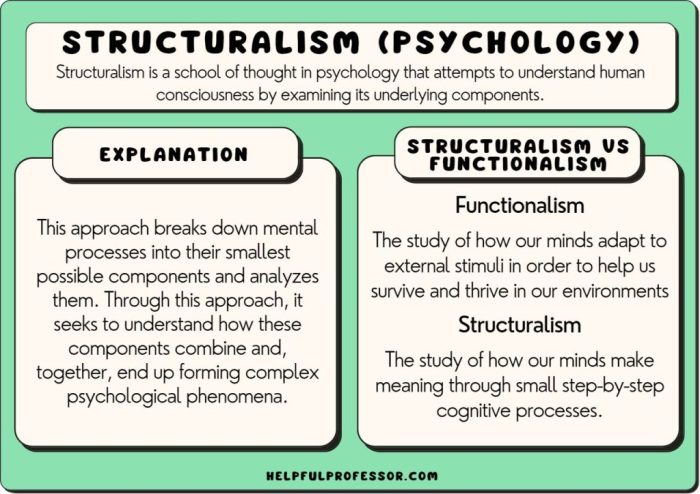
Structuralism, an early school of psychology founded by Wilhelm Wundt, sought to understand the structure of the mind by breaking it down into its constituent elements. However, this approach faced several criticisms that challenged its validity and limited its scope.
Limitations of Structuralism
One major criticism of structuralism was its focus on observable behavior, neglecting the role of internal mental processes. Critics argued that by solely relying on introspection, structuralists overlooked the subjective experiences and unconscious mechanisms that shape human behavior.
Another criticism was structuralism’s emphasis on breaking down mental processes into smaller components. This reductionist approach, it was argued, oversimplified the complexity of the mind and failed to capture the dynamic and holistic nature of psychological phenomena.
Furthermore, structuralism’s reliance on introspection as a research method was questioned. Critics pointed out the potential for bias and subjectivity in self-reporting, which could compromise the validity and reliability of the findings.
Reductionism and Oversimplification
Structuralism’s approach often led to reductionism, oversimplifying complex psychological phenomena. For instance, the reduction of emotions to a set of basic sensations failed to account for the subjective and multifaceted nature of emotional experiences.
Critics also argued that structuralism’s focus on observable behavior missed the dynamic and holistic nature of the mind. It neglected the role of context, culture, and individual differences in shaping psychological processes.
Lack of Ecological Validity, Criticism of structuralism in psychology
Another criticism of structuralism was its lack of ecological validity. The laboratory-based studies conducted by structuralists often lacked real-world relevance. The artificial setting and controlled conditions limited the generalizability of their findings to everyday situations.
For example, structuralists’ studies on reaction time and sensory perception may not apply to complex cognitive tasks or social interactions encountered in real life.
Historical Context and Cultural Bias
Structuralism emerged during a time when scientific objectivity and quantification were highly valued. This historical context influenced the emphasis on observable behavior and the reductionist approach of structuralism.
Moreover, the cultural background of structuralist researchers may have shaped their perspectives. For instance, the focus on introspection and the neglect of cultural influences reflected the individualistic and rationalistic values prevalent in Western society at the time.
Alternative Approaches and Criticisms
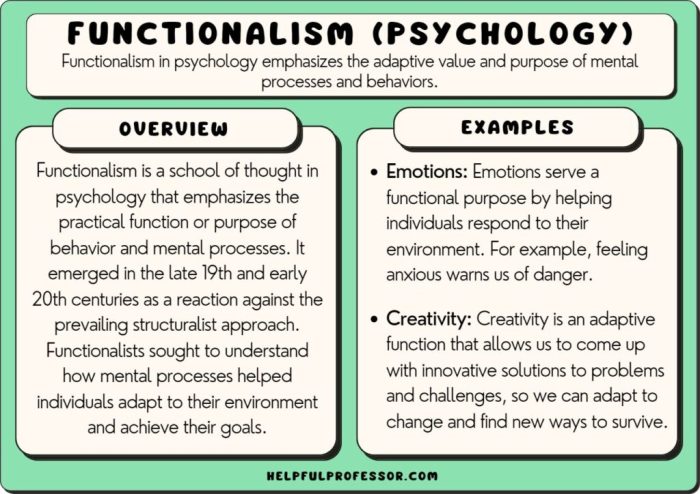
The limitations of structuralism led to the development of alternative psychological approaches, such as functionalism and behaviorism. These approaches criticized structuralism for its focus on static elements of the mind and emphasized the importance of purpose, adaptation, and observable behavior.
Functionalism, led by William James, argued that mental processes serve a purpose and are shaped by their adaptive value. Behaviorism, founded by John B. Watson, rejected introspection and focused solely on observable behavior, considering it the only objective measure of psychological phenomena.
Question & Answer Hub: Criticism Of Structuralism In Psychology
What are the main criticisms of structuralism?
Structuralism has been criticized for its focus on observable behavior, reductionist approach, reliance on introspection, lack of ecological validity, and neglect of individual differences and subjective experiences.
How did structuralism’s limitations contribute to the development of other psychological approaches?
The limitations of structuralism, such as its reductionism and lack of ecological validity, led to the development of alternative approaches such as functionalism and behaviorism, which sought to address these shortcomings.