Ap world history byzantine empire – In the tapestry of world history, the Byzantine Empire stands as a beacon of civilization, its story a captivating narrative of rise, reign, and legacy. From its humble beginnings to its eventual fall, the Byzantine Empire left an enduring mark on the world, shaping the course of history and leaving behind a rich legacy that continues to inspire and intrigue.
This comprehensive exploration of the Byzantine Empire will delve into the factors that fueled its rise, the intricacies of its political and administrative structure, the brilliance of its economic and cultural achievements, and the complexities that led to its decline and fall.
Through a detailed examination of key events, influential figures, and lasting contributions, we will uncover the profound impact of the Byzantine Empire on the development of civilization.
The Rise and Expansion of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire emerged as the eastern half of the Roman Empire following its division in 395 CE. Over the next centuries, it expanded significantly, becoming one of the most powerful and influential empires in history.
Timeline of Byzantine Expansion
- 395 CE:Division of the Roman Empire
- 527-565 CE:Reign of Justinian I; expansion into North Africa, Italy, and parts of Spain
- 6th-7th centuries:Conquests in the Balkans, Middle East, and Asia Minor
- 8th-9th centuries:Loss of territory to Arab and Slavic invasions
- 10th-11th centuries:Reconquest of lost territories and expansion into the Balkans
- 12th-13th centuries:Expansion into Anatolia and the establishment of the Latin Empire
Key Factors Contributing to Byzantine Expansion
- Strong military organization and leadership
- Skilled diplomacy and alliances
- Economic prosperity and trade
- Cultural and religious influence
Major Byzantine Emperors and Their Achievements, Ap world history byzantine empire
| Emperor | Reign | Significant Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Constantine I | 306-337 CE | Established Constantinople as the new capital of the Roman Empire |
| Justinian I | 527-565 CE | Re-conquered North Africa, Italy, and parts of Spain; codified Roman law in the Justinian Code |
| Basil II | 976-1025 CE | Expanded the empire to its greatest extent; known as “the Bulgar-Slayer” |
| Alexios I Komnenos | 1081-1118 CE | Founded the Komnenian dynasty; repelled the First Crusade and stabilized the empire |
The Political and Administrative Structure of the Byzantine Empire
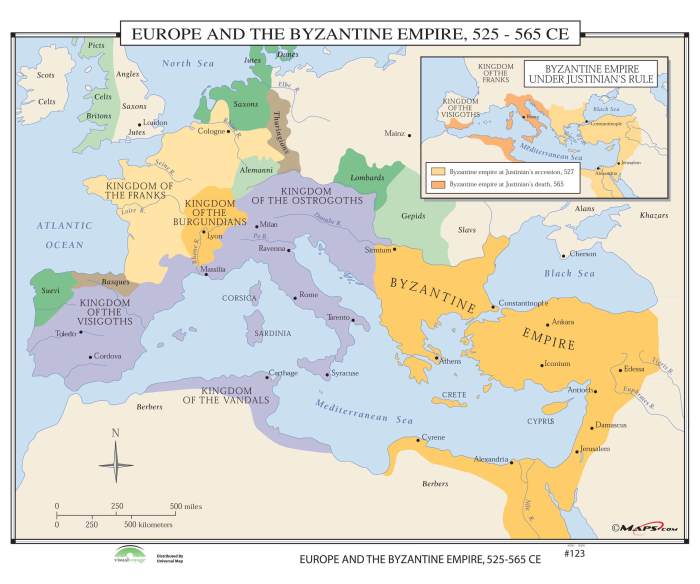
The Byzantine Empire had a unique political and administrative structure that combined elements of Roman and Eastern traditions.
Political Structure
- Emperor:Absolute ruler with both religious and secular authority
- Senate:Advisory body to the emperor
- Bureaucracy:Highly centralized and efficient administrative system
- Church:Closely tied to the state and played a significant role in governance
Comparison to Other Contemporary Empires
| Empire | Political Structure | Emperor’s Role | Bureaucracy | Church’s Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Byzantine Empire | Autocratic monarchy | Absolute ruler with both religious and secular authority | Centralized and efficient | Closely tied to the state and played a significant role in governance |
| Roman Empire | Republic in theory, but increasingly autocratic | Held both religious and secular authority, but shared power with the Senate | Centralized and efficient | Not as closely tied to the state as in the Byzantine Empire |
| Sassanid Empire | Autocratic monarchy | Absolute ruler with both religious and secular authority | Centralized but less efficient than the Byzantine bureaucracy | Zoroastrianism was the official religion, but other religions were tolerated |
| Umayyad Caliphate | Autocratic monarchy | Absolute ruler with both religious and secular authority | Centralized and efficient | Islam was the official religion and played a significant role in governance |
The Economic and Cultural Achievements of the Byzantine Empire
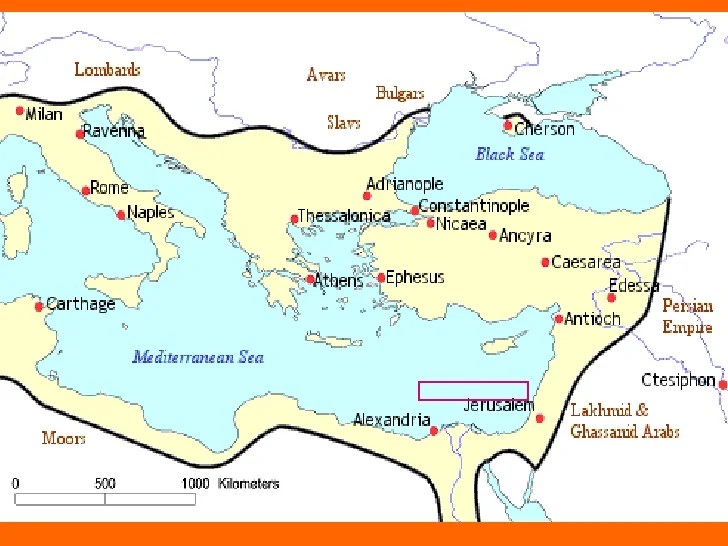
The Byzantine Empire made significant economic and cultural achievements that had a lasting impact on the world.
Economic Achievements
- Trade:The Byzantine Empire was a major trading center, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa
- Agriculture:The empire developed advanced agricultural techniques, such as crop rotation and irrigation
- Currency:The Byzantine Empire introduced the gold solidus, which became the standard currency in Europe for centuries
Cultural Achievements
- Preservation of Classical Knowledge:The Byzantine Empire preserved and transmitted the works of ancient Greek and Roman philosophers, scientists, and artists
- Art:Byzantine art is known for its mosaics, icons, and frescoes
- Architecture:Byzantine architecture is characterized by its use of domes and arches, as seen in the Hagia Sophia
- Literature:Byzantine literature includes works of history, poetry, and theology
The Decline and Fall of the Byzantine Empire: Ap World History Byzantine Empire
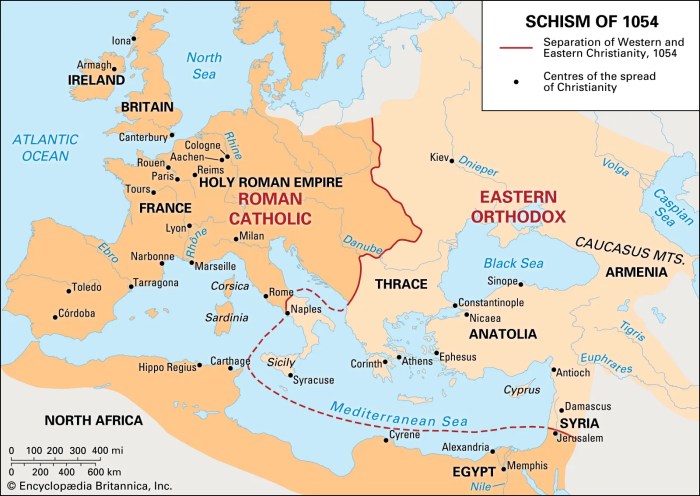
The Byzantine Empire gradually declined from the 11th century onward, culminating in its fall to the Ottoman Turks in 1453.
Factors Contributing to the Decline
- External Pressures:The empire faced constant threats from Arab, Slavic, and Turkish invasions
- Internal Divisions:The empire was plagued by civil wars and religious schisms
- Economic Challenges:The empire’s economy declined due to trade disruptions and the loss of territory
Timeline of Key Events Leading to the Fall of Constantinople
- 1071 CE:Battle of Manzikert; the Byzantines lose control of Anatolia
- 1204 CE:Fourth Crusade; the Byzantine Empire is sacked and divided
- 1261 CE:The Byzantines recapture Constantinople
- 1453 CE:Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks
The Legacy of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire had a profound impact on the development of Europe, Russia, and the Islamic world.
Enduring Contributions
- Preservation of Classical Knowledge:The Byzantine Empire preserved and transmitted the works of ancient Greek and Roman scholars
- Influence on Eastern Europe:The Byzantine Empire introduced Christianity and Cyrillic script to Eastern Europe
- Influence on Russia:The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in the development of Russian culture and religion
- Influence on the Islamic World:Byzantine art and architecture influenced Islamic art and architecture
Common Queries
What were the key factors that contributed to the rise of the Byzantine Empire?
The rise of the Byzantine Empire was fueled by a combination of factors, including its strategic location, strong military, efficient administration, and adoption of Christianity.
What were the major economic and cultural achievements of the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was renowned for its economic prosperity, driven by trade and commerce. It also made significant contributions to art, architecture, literature, and law, preserving and transmitting classical knowledge and culture.
What were the factors that led to the decline and fall of the Byzantine Empire?
The decline and fall of the Byzantine Empire was a complex process influenced by external pressures, internal divisions, economic challenges, and the rise of rival powers.